Static Monitoring Products
| Sensor Type | Description & Applications | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
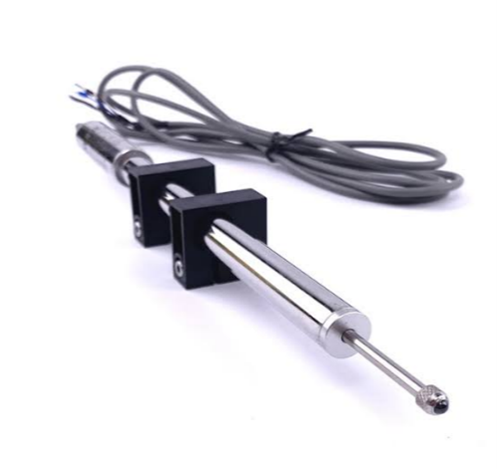 Linear Variable Differential Transformer (LVDT) Sensors |
LVDTs measure linear displacement by detecting changes in the magnetic flux of a ferromagnetic core moving within a coil. The output voltage correlates to the displacement. Applications: Commonly used for monitoring bridge deflections, tunnel deformations, and building subsidence. Ideal for long-term structural health monitoring. |
Highly precise, non-contact, and suitable for harsh environments. |
 Strain Gauges |
Strain gauges measure small deformations or strains in structural components by detecting changes in resistance when a material is stretched or compressed. Applications: Used in monitoring strain in beams, columns, and structural joints in bridges, buildings, and dams. |
Compact and capable of measuring minute strain changes with high accuracy. |
 Optical Displacement Sensors (Fiber Optic Sensors) |
These sensors measure displacement through light transmission changes in fiber optic cables. Based on the Bragg Grating principle, changes in strain alter the wavelength of reflected light. Applications: Widely used for long-distance, real-time monitoring of bridges, tunnels, and dams. |
Ideal for large-scale, long-distance measurements with high sensitivity. |
 Laser Displacement Sensors |
These sensors use laser beams to measure the distance between the sensor and the target. The time for the laser to reflect back provides displacement data. Applications: Ideal for monitoring structural movement, cracks, and surface deformation in civil infrastructure projects. |
Non-contact, high-precision, and effective for crack monitoring. |



 SPPL India
SPPL India